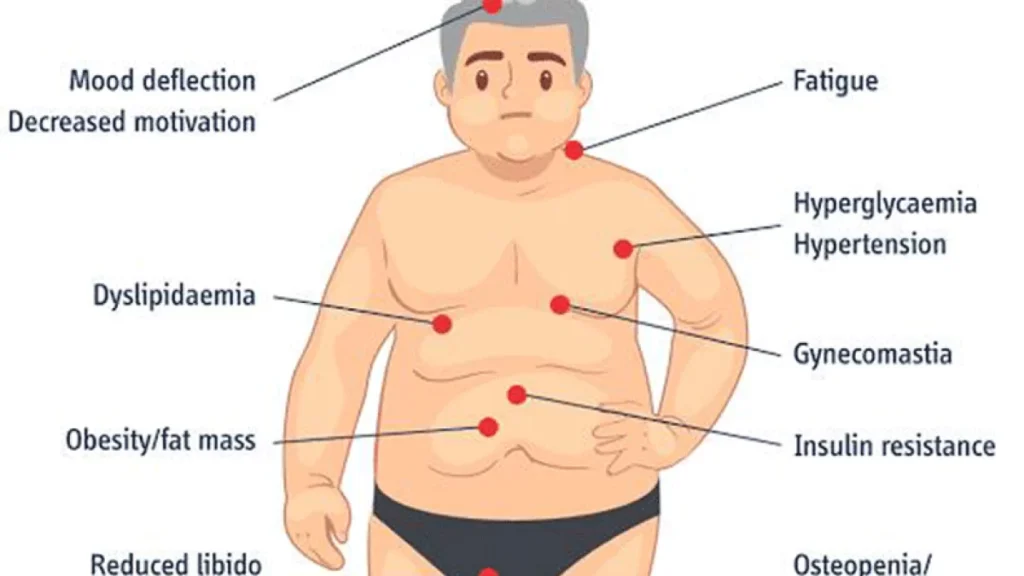
Low testosterone, also known as male hypogonadism, is a condition where the body doesn’t produce enough of the hormone that plays a central role in male health. Testosterone is essential for energy, muscle mass, sex drive, bone strength, and overall well-being. When levels drop too low, men can feel it — physically, mentally, and emotionally.
There are two main types of hypogonadism: primary and central.
Primary vs. Central Hypogonadism
Primary hypogonadism happens when the testicles themselves aren’t working properly. This could be due to injury, illness, or a genetic condition. In these cases, the body sends the right signals to produce testosterone, but the testes can’t respond.
Central hypogonadism, on the other hand, is caused by problems in the brain — specifically the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, which are responsible for sending signals to the testes. If these signals are weak or absent, testosterone production slows down or stops.
Both types can lead to low testosterone levels and similar symptoms.
Symptoms of Low Testosterone
Men with hypogonadism might notice:
-
Low sex drive
-
Erectile dysfunction
-
Fatigue and low energy
-
Loss of muscle mass
-
Increased body fat
-
Mood swings or depression
-
Thinner bones or lower bone density
-
Trouble concentrating
In central hypogonadism, there might also be other signs linked to hormone imbalance. These can include:
-
Headaches
-
Vision changes
-
Milky discharge from the nipples (a condition called galactorrhea)
In some cases, these symptoms could be caused by a pituitary tumor or other issues in the brain that affect hormone regulation.
How Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) Helps
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT) is the most common treatment for men with confirmed low testosterone levels. It works by restoring hormone levels to a normal range and improving symptoms like fatigue, low libido, and mood changes.
TRT is often prescribed in cases of primary hypogonadism, or when testosterone levels fall with age and symptoms interfere with daily life.
How TRT Is Given
There are several ways to take testosterone, including:
-
Injections (weekly or biweekly)
-
Gels or creams (applied daily to the skin)
-
Skin patches
-
Oral tablets or nasal sprays (less commonly used)
Each method has pros and cons, and the right one depends on your symptoms, lifestyle, and medical history.
Does TRT Work?
Yes — for the right person, TRT can make a noticeable difference. Most men feel more energetic, sleep better, have a stronger sex drive, and regain motivation. Muscle tone and mental clarity often improve too.
But TRT isn’t a cure-all. It should only be used in men who have both low testosterone levels confirmed by blood tests and symptoms that affect quality of life.
Risks and Monitoring
Like all medications, testosterone therapy comes with some risks. Possible side effects include:
-
Increased red blood cell count (which can raise the risk of blood clots)
-
Acne or oily skin
-
Breast swelling or tenderness
-
Sleep apnea worsening
-
Reduced sperm production (affecting fertility)
Because of these risks, regular follow-up and blood tests are essential. Your doctor will check hormone levels, blood counts, and monitor for any adverse effects.
Guidelines from Experts
In 2020, the American College of Physicians (ACP) released clear guidelines on testosterone therapy for men with age-related testosterone decline. They emphasized that:
-
TRT should only be offered if both low testosterone and relevant symptoms are present.
-
The decision to start treatment should involve a full evaluation and discussion with the patient.
-
Ongoing monitoring is important to ensure safety and effectiveness.
These guidelines are backed by respected medical bodies like the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), making them a reliable standard for care.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes male hypogonadism?
It can be caused by testicular damage (primary) or by the brain not sending the right hormone signals (central). Aging, illness, injury, or tumors can all play a role.
Is low testosterone always a problem?
Not necessarily. Some men have low levels without symptoms and don’t need treatment. But if you’re feeling tired, unmotivated, or experiencing sexual health changes, it’s worth testing your levels.
Can TRT help improve fertility?
Not directly. In fact, TRT can reduce sperm production. If you’re trying to conceive, alternatives like hcg may be better — talk to a doctor who specializes in men’s health.
How do I know if TRT is right for me?
You’ll need both low testosterone on a blood test and symptoms that interfere with daily life. Your doctor will help weigh the benefits and risks.
Is testosterone therapy safe long term?
For many men, yes — if monitored properly. It’s important to follow up regularly with your provider and check hormone levels, blood pressure, and blood counts.